Once the devices are connected and data from the devices is made available to the core platform, the monitoring part kicks in. The device data is usually stored in a database (possibly a time series database) for further analysis and predictions and at the same time can be acted upon by the system for real-time analysis. The monitoring phase typically involves providing a dashboard to track the devices remotely across the globe and how each device is being utilized as per the specification. The specifications are available as part of the metadata we talked about it earlier in Asset Management section.
For instance, in the case of the r elevator use case, the optimum motor temperature should not be more than 40 degree Celsius or the air condition temperature inside the elevator should be at least 18 degree Celsius at peak load.
Monitoring can also be used to detect if the elevators are installed and functioning as per the specification. For instance, every manufacturer provides a checklist for regular maintenance activity that can be tracked through remote monitoring. The following is a sample checklist, which is provided by the City of Chicago – Department of Buildings for compliance purpose. As you see, most of the test requirements can be handled by adding sensors and monitoring it remotely.
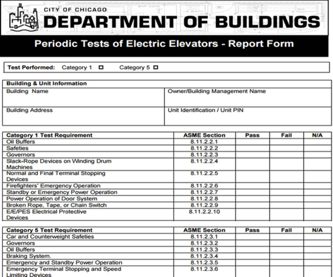
In the future, environmental requirements like energy efficiency, passenger safety, and control compliance can be met through the remote monitoring and used for auditing and inspection eventually.
As the manufacturers start embracing IoT with the concept of connected products in mind, we would see a new class of products in future that will change the complete dynamics of manufacturing process. Imagine a self-test on the elevator which automatically evaluates the compliance parameters and publishes a report as part of the audit and quality procedures in a connected environment. (In short, an elevator would be compliant and secured 24 * 7).
Once the systems and devices are being monitored, next step is to use the information to provide timely maintenance of the assets based on the specification and its operating condition. We refer to it as condition-based maintenance.