Large manufacturers have been using some automation and smart technology to streamline and optimize their processes and improve their operation and production efficiency. However, as manufacturers start moving towards the next industrial revolution (Industry 4.0 or Industrial Internet of Things(IIoT)) and technologies available today that can analyze massive volume, variety, and velocity of data generated by various machines and sensors, there arises an opportunity to streamline this information to further improve the manufacturing process and most importantly start designing and developing connected products that can enhance customer satisfaction and services and open up avenues for new financial business models.
Note – The term Industry 4.0 and Industrial Internet of Things are usually used interchangeably, but they have different context and reference. Industry 4.0 is a term coined by the German government, it marks the fourth industrial revolution and can be described as the digitalization of industrial sector, especially for manufacturing. Industrial Internet of Things is about enabling and applying IoT across industries. Also check out Industrial Internet Consortium (http://www.industrialinternetconsortium.org/) a non-profit organization, founded by AT&T, Cisco, GE, IBM and Intel to collaborate and set the architectural framework and direction for the Industrial Internet of Things
Let’s take an example of a leading elevator manufacturing company which supplies elevators across the globe. The elevators already have some instrumentation built in, like door sensor, a weight sensor which triggers an alert like beep in case of overload, etc., but the elevator company has no visibility on how the elevators are being used across the globe and therefore, raises the following important questions:
Are these elevators working as expected and utilized as per the specification?
Is there a failure condition?
What kind of failure has occurred?
How are failures to be handled?
What is the typical acceptable downtime?
Which agency is handling the failure condition?
How effective is the after-sales service in that region?
Is there a competent expertise available to handle a given failure condition?
Are the spare parts available to quickly start the restoration process?
Proper application of IoT can address the above questions by designing a connected solution that will help capture and analyze the product usage, operational and failure data and ultimately improve the customer satisfaction and services.
IoT can not only transform the end products but the entire manufacturing process right from the start where the elevators are manufactured. The supply chain process and logistics can also be streamlined to enhance operational efficiency and productivity and deliver better financial gains.
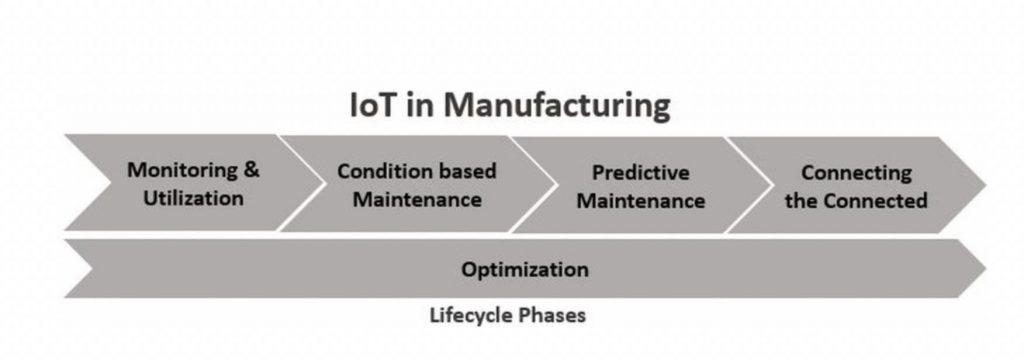
IoT is an incremental journey; it’s an evolution, and any manufacturing IoT realization can be broken down into the following five phases:
- Monitoring & Utilization
- Condition based maintenance
- Predictive Maintenance
- Optimization
- Connecting ‘connected solutions.’