In this step, we would create Cloud NAT. Cloud NAT allows VMs instances without external IP addresses and private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters to connect to the Internet.
Cloud NAT implements outbound NAT (i.e. network translation, mapping internal IP addresses to external IP) to allow instances to reach the Internet.
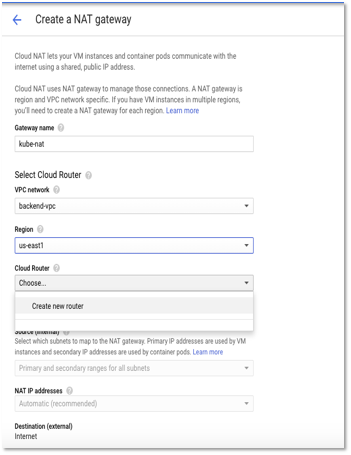
Go to Network Services – > Cloud NAT – > Create NAT Gateway
- Enter a name for gateway and select VPC network as backend-vpc (created in Step 1).
- Select the region as us-east 1 (same as the VPC region).
Figure 8 – Create NAT Gateway
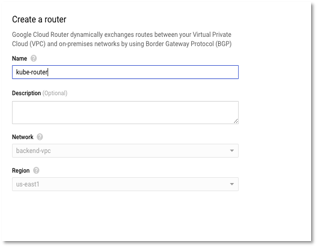
- Click create new Cloud router. Enter the name and click continue. Cloud Router enables dynamic routing for the VPC. For more details, kindly refer to https://cloud.google.com/router/docs/concepts/overview.
Figure 9 – Create Router
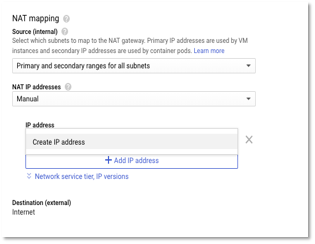
- In the NAT mapping, select Manual NAT IP address. We don’t select automatic as we would like to reserve a set of IPs that we can provide to external services/partners to whitelist on their servers. Choosing automatic would create and release IP based on workloads.
Figure 10 – Create NAT Mapping
- Select Create IP address and enter the name of the IP address.
Figure 11 – Create Static IP address
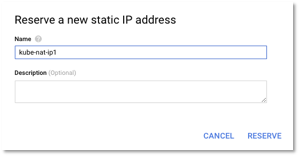
- Similarly, create one more IP address. Two external outbound IPs are sufficient for our network. You can add new IPs based later, if you identify bottlenecks (through monitoring) in your network.
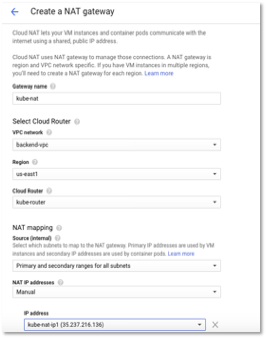
- The following image shows the summary of NAT configuration. Click create.
Figure 12 – NAT Gateway configuration
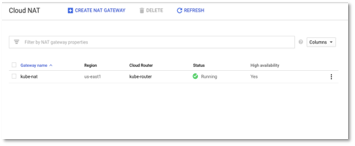
- Once created, wait until the status is Running for changes to be effective.
Figure 13 – Cloud NAT Status